Introduction
LinkedIn ads are a form of advertising on the professional networking platform LinkedIn. They allow businesses and individuals to promote their products, services, or content to a targeted audience of LinkedIn users. These ads appear in various formats, including sponsored content in users’ feeds, sponsored InMail messages, display ads on the LinkedIn site, and dynamic ads personalized for the viewer.
LinkedIn ads offer precise targeting options based on criteria such as job title, industry, company size, skills, and more. This enables advertisers to reach specific professional demographics, making it a powerful tool for B2B (business-to-business) marketing. The platform also provides analytics and insights, allowing advertisers to track the performance of their campaigns and make data-driven decisions.
LinkedIn ads can be set up through the LinkedIn Campaign Manager, where advertisers define their objectives, target audience, budget, and bidding strategy. The platform supports various ad formats, including single image ads, carousel ads, video ads, and more. Advertisers can also utilize sponsored InMail to send personalized messages directly to their target audience.
The cost of LinkedIn ads varies based on the bidding model chosen, such as cost per click (CPC) or cost per impression (CPM). The bidding process involves competing with other advertisers targeting the same audience, and the ad with the highest bid and relevance typically wins the opportunity to be displayed.
In summary, LinkedIn ads are a comprehensive advertising solution for businesses and professionals looking to promote their offerings to a tailored audience within the LinkedIn ecosystem. The platform’s focus on professional networking makes it especially effective for reaching decision-makers and professionals in specific industries.
LinkedIn Ad Objectives

LinkedIn ads support various objectives to cater to different marketing goals. Some common LinkedIn ad objectives include:
1. Brand Awareness: The objective is to boost recognition and visibility. Employ visually appealing content to make a memorable impact on a broad audience.
2. Website Visits: Aimed at driving traffic to an external site, this objective requires compelling ad copy and visuals, including a clear call-to-action (CTA), to prompt users to click through to the designated website or landing page.
3. Engagement: Focused on increasing interaction, create content that stimulates likes, comments, and shares. Utilize questions, industry insights, or compelling visuals to spark engagement.
4. Video Views: Targeted at increasing views for video content, craft engaging videos using storytelling, animation, or demonstrations to captivate the audience.
5. Lead Generation: Collect leads directly on LinkedIn using sponsored content with lead generation forms, streamlining the process for users to submit their information without leaving the platform.
6. Website Conversions: Drive specific actions on an external website using conversion tracking and a strong call-to-action. Promote content or offers that encourage users to take the desired action.
7. Job Applicants: Attract candidates by featuring compelling job listings with clear descriptions and highlighting your company culture to entice the right candidates.
8. Followers: Increase followers on your LinkedIn Company Page by showcasing the value of following your company and featuring updates, achievements, and exclusive content.
9. Brand Consideration: Encourage users to consider your brand by sharing content highlighting unique selling points, achievements, or customer testimonials to build credibility and trust.
10. Event Attendance: Drive registrations and attendance for events by featuring compelling event details, benefits, and exclusive content, and include a clear call-to-action to encourage users to register or RSVP.
LinkedIn ads benefits
LinkedIn ads offer unique benefits for businesses looking to reach a professional audience. One key advantage is precise targeting, allowing advertisers to tailor their campaigns based on factors such as job title, industry, and company size. This granular targeting ensures that ads are seen by the right professionals, increasing the likelihood of engagement.
Additionally, LinkedIn’s platform emphasizes credibility, as it is a trusted network for career professionals. This can enhance the perceived value of advertised products or services. Moreover, LinkedIn’s sponsored content and InMail options provide diverse formats for effective storytelling and direct communication.
Overall, leveraging LinkedIn ads can be instrumental in generating leads, building brand awareness, and fostering B2B connections in a professional context.
1. Targeted Reach: LinkedIn provides precise targeting options based on job title, industry, company size, skills, and more. This allows advertisers to reach a specific professional audience, making it effective for B2B marketing.
2. Professional Audience: With over 700 million professionals, LinkedIn is a platform where decision-makers and professionals engage. This makes it an ideal space for businesses targeting a professional audience.
3. Diverse Ad Formats: LinkedIn supports various ad formats, including sponsored content, sponsored InMail, display ads, and dynamic ads. Advertisers can choose the format that best suits their campaign goals and content type.
4. Analytics and Insights: LinkedIn’s Campaign Manager provides robust analytics, allowing advertisers to track the performance of their campaigns. Insights include metrics like clicks, impressions, engagement, and conversions, enabling data-driven decision-making.
5. Lead Generation Forms: LinkedIn ads can include lead generation forms, simplifying the process for users to submit their information without leaving the platform. This is valuable for collecting leads directly within the professional network.
6. Brand Visibility: LinkedIn ads enhance brand visibility and recognition among a professional audience, contributing to brand building and awareness within relevant industries.
7. Job Advertising: For recruiting purposes, LinkedIn ads enable companies to promote job opportunities and attract potential candidates directly on the platform, tapping into the professional network for talent acquisition.
8. Networking Opportunities: Beyond direct advertising, LinkedIn provides opportunities for organic networking. Companies can engage with professionals through their Company Page, showcasing industry expertise and building relationships.
9. Event Promotion: LinkedIn ads can effectively promote events, driving registrations and attendance. This is valuable for webinars, conferences, product launches, and other business-related events.
10. Customizable Budgets: Advertisers have control over their budgets, with options for daily or total campaign spending. This flexibility allows businesses of various sizes to participate in LinkedIn advertising.
LinkedIn ads for lead generation
LinkedIn ads are highly effective for lead generation due to the platform’s professional user base and targeted advertising options. Here’s a tailored approach for using LinkedIn ads specifically for lead generation:
1. Sponsored Content with Lead Gen Forms: Create sponsored content that highlights your offering or content piece. Use lead generation forms within the ad to collect information directly on LinkedIn. Keep the form concise, requesting only essential information to improve completion rates.
2. Precise Targeting: Utilize LinkedIn’s robust targeting options to pinpoint your ideal audience. Define criteria such as job title, industry, company size, and skills relevant to your target leads.
3. Compelling Ad Copy and Visuals: Craft compelling ad copy that clearly communicates the value proposition. Use eye-catching visuals to capture attention within the professional feed.
4. Clear Call-to-Action (CTA): Include a clear and compelling CTA in your ad, directing users to take the next step. Clearly communicate what users can expect after filling out the form.
5. Dynamic Ads: Consider using dynamic ads that automatically personalize content for each viewer. This personalization can enhance engagement and increase the likelihood of lead generation.
6. Test and Optimize: A/B test different ad variations to understand what resonates best with your target audience. Continuously optimize your campaign based on performance metrics and user engagement.
7. Follow-Up with InMail: For high-value leads, consider using sponsored InMail messages for personalized follow-ups. Craft messages that continue the conversation and provide additional information.
8. Conversion Tracking: Implement conversion tracking to measure the effectiveness of your lead generation campaigns. Understand which ads and targeting criteria are driving the most valuable leads.
9. Budget Management: Set a budget that aligns with your lead generation goals. Monitor spending and adjust budgets based on performance and lead acquisition costs.
10. Nurture Leads on LinkedIn: Two things to look out for:
– Engage with leads directly on LinkedIn by sharing relevant content and participating in conversations.
– Use the platform to build relationships and establish your brand as a trusted authority.
What is linkedin ads manager?
LinkedIn Ads Manager is the platform’s advertising management tool that allows users to create, manage, and analyze their LinkedIn advertising campaigns. It provides a user-friendly interface for advertisers to set up various types of ads, target specific audiences, and track the performance of their campaigns. Here are key features and functionalities of LinkedIn Ads Manager:
1. Campaign Creation: Users can create new advertising campaigns and choose their campaign objective based on goals such as brand awareness, lead generation, website visits, and more.
2. Ad Format Selection: LinkedIn Ads Manager supports different ad formats, including sponsored content, sponsored InMail, display ads, and dynamic ads. Advertisers can choose the format that aligns with their campaign objectives and content type.
3. Audience Targeting: Precise targeting options allow advertisers to define their audience based on criteria such as job title, industry, company size, skills, and more. This ensures that ads reach a specific and relevant professional audience.
4. Budget Management: Advertisers can set a daily or total budget for their campaigns. This flexibility enables businesses of various sizes to participate in LinkedIn advertising, and it allows for budget adjustments based on campaign performance.
5. Bidding Strategy: LinkedIn Ads Manager provides bidding options such as cost per click (CPC) and cost per impression (CPM). Advertisers can choose the bidding strategy that aligns with their goals and budget.
6. Ad Placement: Advertisers can select where their ads appear, whether in the LinkedIn feed, on the right rail, or on LinkedIn partner sites. This helps tailor the ad placement to the campaign objectives.
7. Ad Creative: Users can upload images, create headlines, write ad copy, and add a call-to-action to craft compelling and visually appealing ads.
8. Conversion Tracking: LinkedIn Ads Manager includes conversion tracking tools to measure the impact of ads on specific actions such as form submissions, sign-ups, or purchases on external websites.
9. Analytics and Reporting: Robust analytics and reporting features allow advertisers to track key performance metrics, such as clicks, impressions, engagement, and conversions. This data helps in evaluating the success of the campaigns.
10. Campaign Optimization: Advertisers can monitor campaign performance and make real-time adjustments to optimize for better results. This may include refining targeting criteria, adjusting bids, or updating ad creative.
What are linkedIn ads types?
LinkedIn offers various types of ads to cater to different marketing goals and content formats. The main types of LinkedIn ads include:
1. Sponsored Content: These ads appear in users’ LinkedIn feeds and look like regular posts. They can include text, images, and links, making them effective for brand awareness, lead generation, and promoting articles or blog posts.
2. Sponsored InMail: This ad type enables advertisers to send personalized messages directly to the LinkedIn inboxes of their target audience. It is often used for lead generation, event promotion, or delivering personalized content.
3. Display Ads: Appearing on the right side of the LinkedIn desktop interface, display ads include images and text. They are suitable for promoting events, webinars, or general brand awareness.
4. Dynamic Ads: Automatically personalizing content for each viewer based on their LinkedIn profile data, dynamic ads are highly customizable. They are effective for promoting job opportunities, events, or personalized content.
5. Text Ads: Simple, text-only ads that appear at the top of the LinkedIn desktop interface. They are cost-effective and suitable for promoting content, driving traffic to a website, or generating leads.
6. Carousel Ads: This format allows advertisers to showcase multiple images or cards within a single ad. Users can scroll through the carousel to view different images and information, making it engaging for storytelling or showcasing product features.
7. Conversation Ads: Interactive messages that guide users through a series of questions or options. They are effective for starting conversations or gathering insights.
8. LinkedIn Video Ads: These ads allow advertisers to share video content with their audience. They can be used for brand storytelling, product demonstrations, or sharing thought leadership content.
9. Lead Gen Forms: Integrated forms within LinkedIn ads, allowing users to submit their information without leaving the platform. These forms simplify the lead generation process and are commonly used for capturing contact details.
10. Job Ads: Specifically designed for recruiting and promoting job opportunities, these ads appear on the LinkedIn Jobs page. They can be targeted to specific demographics based on job preferences and qualifications.
7 LinkedIn ads best practices to try

1. Precise Audience Targeting: Leverage LinkedIn’s detailed targeting options to define your audience based on job titles, industries, company size, and more. This ensures your ads reach a specific and relevant professional audience, improving the effectiveness of your campaigns.
2. Compelling Visuals and Copy: Capture attention with visually appealing images or videos, accompanied by concise and compelling ad copy. Clearly communicate your value proposition and use a strong call-to-action (CTA) to prompt user engagement.
3. A/B Testing: Experiment with different ad variations to understand what resonates best with your audience. Test different headlines, visuals, ad copy, and CTAs to optimize for the highest performance. Regularly analyze results and make data-driven adjustments.
4. Lead Generation Forms: Utilize LinkedIn’s built-in lead generation forms to simplify the process for users to submit their information. Ensure your forms are concise, requesting only essential information, and clearly communicate the value users will receive in return.
5. Dynamic Ads for Personalization: Explore dynamic ads to automatically personalize content based on the viewer’s LinkedIn profile data. This personalization can enhance engagement and make your ads more relevant to individual users.
6. Conversion Tracking: Implement conversion tracking to measure the impact of your ads on specific actions, such as form submissions or website visits. This data is crucial for understanding the success of your campaigns and optimizing for better results.
7. Strategic Use of Sponsored InMail: When using Sponsored InMail, personalize your messages and focus on providing value to the recipient. Craft messages that resonate with your target audience and include a clear CTA. Use Sponsored InMail for targeted outreach in lead generation or event promotion.
LinkedIn ads examples
Sponsored Content:
Single Image Ads: These ads are designed to feature a compelling image alongside a concise caption and a direct link. They serve as effective tools for promoting content such as articles, blog posts, or any other material that benefits from visual engagement. The single-image format allows for a clear, focused message to be delivered directly to the target audience in their LinkedIn feeds.
Carousel Ads: Building upon the concept of single image ads, carousel ads enable the display of multiple images that users can scroll through. This format is particularly useful for telling a sequential story, showcasing various product features, or presenting a diverse range of content. By leveraging a carousel, advertisers can maintain user attention and convey a more comprehensive message.
Sponsored InMail:
Personalized Messages: Sponsored InMail ads provide a direct avenue to users’ LinkedIn inboxes. These messages are highly customizable, allowing for personalization of content, inclusion of images, and the integration of call-to-action buttons. This format is effective for delivering targeted and personalized marketing messages, facilitating direct communication with potential leads or customers.
Sponsored Video Ads:
Native Video Ads: In the era of visual content, native video ads on LinkedIn offer a dynamic way to engage the audience. These videos seamlessly integrate into the LinkedIn feed, making them an excellent choice for product demonstrations, customer testimonials, or broader brand storytelling. The immersive nature of video content enhances the overall impact of the marketing message.
Dynamic Ads:
Follower Ads: Dynamic ads on LinkedIn include Follower Ads, which aim to promote a company’s LinkedIn page to a specific target audience. The objective is to increase the number of followers for the page. This format is beneficial for enhancing brand visibility and fostering a community around the company.
Job Ads: Another facet of dynamic ads is the promotion of job openings. These targeted ads aim to reach users with specific demographics matching the requirements of the job listings. This feature facilitates efficient recruitment efforts by connecting with relevant professionals on the platform.
Display Ads:
Display Image Ads: Positioned traditionally on the right side of the LinkedIn homepage or user profile pages, display image ads serve as classic banner advertisements. While they are not as interactive as some other formats, they offer a consistent and visible presence, providing an additional channel for brand exposure.
Lead Gen Forms:
Lead Generation Ads: LinkedIn’s lead generation ads incorporate a call-to-action button that, when clicked, opens a pre-filled form with the user’s LinkedIn information. This streamlines the process of collecting user data, such as email addresses, making it easier for users to engage with the advertised content without leaving the LinkedIn platform.
Text Ads:
Text Ads with Images: Text ads on LinkedIn, when complemented with images, create a visually appealing yet concise promotional format. These ads typically appear at the top or right side of the LinkedIn homepage. The combination of succinct text and a relevant image aims to capture user attention efficiently, sparking interest in the promoted content or offering.
LinkedIn ads benchmarks
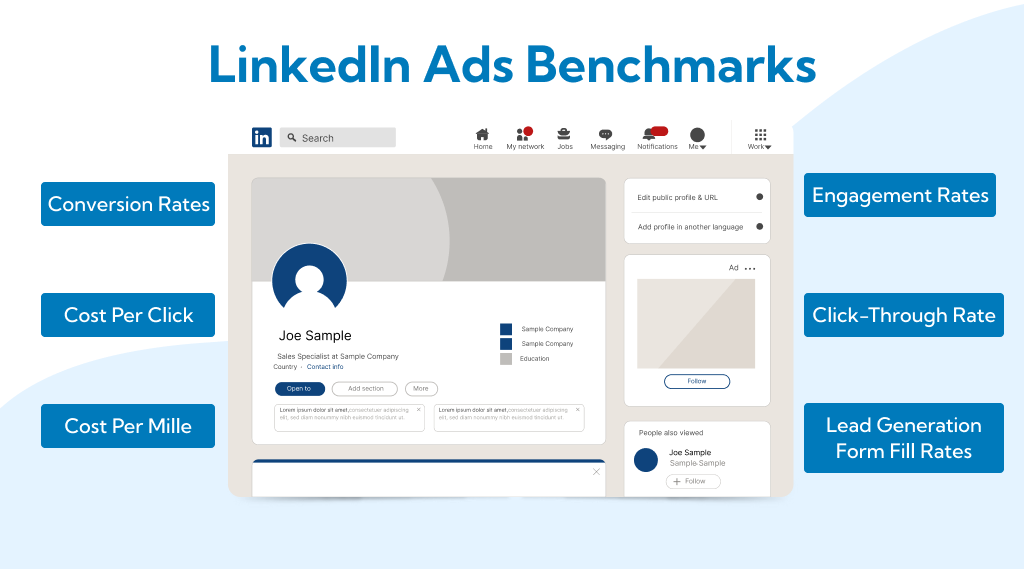
Navigating the landscape of LinkedIn advertising requires a keen understanding of key performance metrics. Benchmarks serve as invaluable guides, providing insights into the average performance indicators across various aspects of LinkedIn ads.
From Click-Through Rates (CTR) and Conversion Rates to Cost Per Click (CPC) and Engagement Rates, these benchmarks offer advertisers a compass to gauge the effectiveness of their campaigns.
Delving into each metric reveals nuances that can impact the success of LinkedIn ads, helping businesses refine their strategies for optimal results. In this dynamic realm where precision meets creativity, staying attuned to these benchmarks empowers advertisers to make informed decisions, ensuring their LinkedIn campaigns resonate with target audiences and achieve desired outcomes.
1. Click-Through Rate (CTR):
The Click-Through Rate (CTR) for LinkedIn ads typically ranges between 0.5% and 2%. This metric measures the percentage of users who clicked on an ad after seeing it. A CTR within this range is considered average, but actual performance can vary based on factors like industry, ad content, and targeting specificity. Higher CTRs often indicate more engaging and relevant ads.
2. Conversion Rates:
Conversion rates on LinkedIn ads, representing the percentage of users who completed a desired action after clicking on an ad, commonly range from 2% to 5%. This action could include filling out a form, downloading content, or making a purchase. Advertisers aim to optimize conversion rates by creating compelling ad content and ensuring a seamless user experience post-click.
3. Cost Per Click (CPC):
The Cost Per Click (CPC) for LinkedIn ads typically falls between $2 and $5, although this figure can fluctuate based on industry competitiveness, targeting parameters, and the quality of the ad campaign. A lower CPC is generally desirable as it indicates cost-effectiveness in acquiring clicks. Advertisers often optimize campaigns to achieve a balance between cost and performance.
4. Cost Per Mille (CPM):
Cost Per Mille (CPM), representing the cost per thousand impressions, varies between $8 and $15 on LinkedIn. CPM is influenced by factors such as industry demand, ad relevance, and targeting precision. Advertisers monitor CPM to assess the cost of reaching a thousand users with their ad, providing insights into the efficiency of their campaign’s visibility.
5. Engagement Rates:
Engagement rates on LinkedIn ads, encompassing likes, comments, and shares, typically range from 0.1% to 0.3%. A higher engagement rate indicates that the audience is actively interacting with the ad content. Advertisers often prioritize creating engaging and shareable content to boost these metrics and extend the reach of their campaigns through organic interactions.
6. Lead Generation Form Fill Rates:
For LinkedIn’s lead generation forms, where users can submit information directly through the ad, a reasonable benchmark for form fill rates is around 10% to 20%. Advertisers aim to optimize this metric by designing forms that are concise, relevant, and aligned with the user’s expectations. A higher form fill rate indicates successful lead generation.
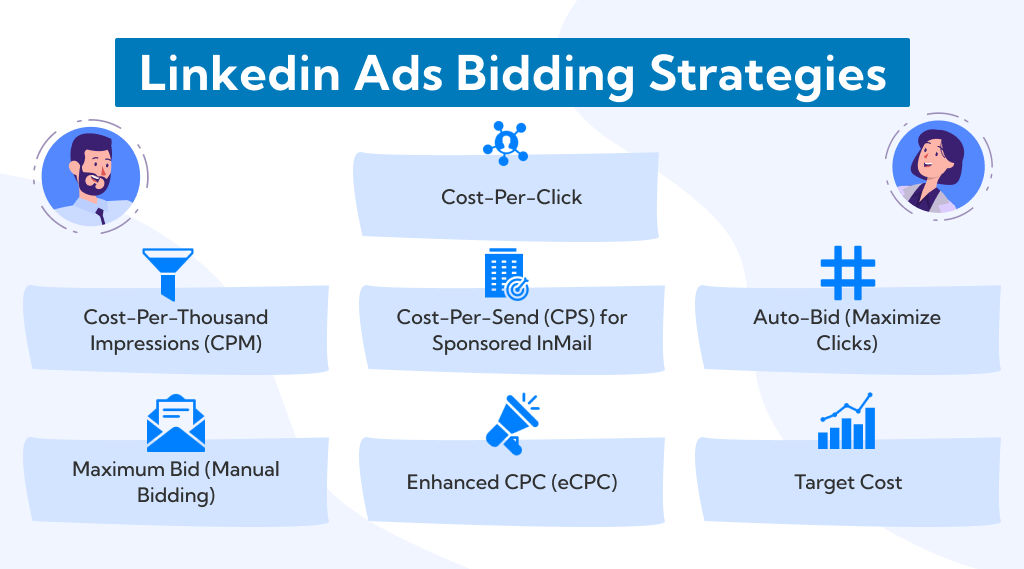
What are some linkedin ads bidding strategies to try?
LinkedIn offers different bidding strategies to help advertisers maximize the effectiveness of their campaigns. The choice of bidding strategy depends on your campaign goals and budget. Here are some LinkedIn ads bidding strategies to consider:
1. Cost-Per-Click (CPC):
Description: With CPC bidding, you pay for each click on your ad. This strategy is effective if your goal is to drive website traffic, generate leads, or increase engagement.
When to Use: Suitable when your primary focus is on user interaction and you want to control costs associated with actual clicks.
2. Cost-Per-Thousand Impressions (CPM):
Description: CPM bidding involves paying for every thousand impressions (views) of your ad, regardless of clicks. This is beneficial for increasing brand visibility.
When to Use: Ideal when the goal is to maximize ad exposure and brand awareness. It’s particularly useful for campaigns focused on creating brand recognition.
3. Cost-Per-Send (CPS) for Sponsored InMail:
Description: This bidding strategy is specific to Sponsored InMail campaigns. You pay for each InMail message delivered.
When to Use: Suitable for direct and personalized communication with targeted LinkedIn users. Effective for promoting events, webinars, or personalized content.
4. Auto-Bid (Maximize Clicks):
Description: LinkedIn’s Auto-Bid feature automatically adjusts your bid to get the most clicks within your daily or lifetime budget.
When to Use: A hands-off approach for advertisers who want LinkedIn to optimize bids for maximum clicks while staying within their specified budget.
5. Maximum Bid (Manual Bidding):
Description: Allows you to set the maximum amount you’re willing to pay for a click or 1,000 impressions. Provides more control over your bidding strategy.
When to Use: Useful when you have specific bid constraints or want precise control over how much you’re willing to spend for each interaction or impression.
6. Enhanced CPC (eCPC):
Description: LinkedIn’s Enhanced CPC automatically adjusts your bid for clicks that are more likely to convert into leads.
When to Use: Effective when the primary goal is lead generation. LinkedIn’s algorithm optimizes bids based on historical data to prioritize clicks likely to result in conversions.
7. Target Cost:
Description: This bidding strategy allows you to set a target cost per click or per thousand impressions. LinkedIn aims to keep your average cost around your specified target.
When to Use: Useful when you have a specific target cost in mind and want to maintain a consistent average cost per click or impression.
LinkedIn ads Vs google ads for b2b Saas : which is better?
The choice between LinkedIn Ads and Google Ads for B2B SaaS (Software as a Service) depends on various factors, and both platforms can play complementary roles in a comprehensive digital marketing strategy. Here’s a comparison to help you make an informed decision:
LinkedIn Ads for B2B SaaS:
Pros:
1. Targeted Audience: LinkedIn allows precise targeting based on professional demographics such as job title, industry, company size, and seniority. This is particularly advantageous for B2B marketing, where reaching decision-makers is crucial.
2. Business-Focused Environment: LinkedIn is a professional network, making it an ideal platform for B2B marketing. Professionals often engage with content related to their industry and business needs.
3. Lead Generation Forms: LinkedIn offers lead generation forms within the platform, simplifying the process for users to provide their information, which is valuable for B2B lead generation.
Cons:
1. Higher CPC: Compared to Google Ads, LinkedIn Ads generally have a higher Cost Per Click (CPC). Advertisers need to consider their budget constraints and the potential return on investment.
Google Ads for B2B SaaS:
Pros:
1. Intent-Based Search: Google Ads operate on a search-based model, allowing you to target users actively searching for solutions related to your B2B SaaS offering. This means you can reach potential customers when they are actively seeking information.
2. Keyword Targeting: Google Ads enable precise targeting based on keywords, ensuring that your ads appear in relevant search queries.
3. Diverse Ad Formats: Google Ads offer various formats, including text ads, display ads, and video ads, providing flexibility in how you present your B2B SaaS solution.
Cons:
1. Competition: The B2B SaaS landscape on Google Ads can be highly competitive, leading to increased bidding costs for certain keywords.
2. Limited Professional Demographics: While you can target by demographics to some extent, Google Ads primarily rely on user behavior and search intent, which may not be as business-focused as LinkedIn.
Choosing the Right Approach:
1. Combined Strategy: Many B2B SaaS businesses find success in combining both LinkedIn Ads and Google Ads. LinkedIn can be effective for targeting specific roles and industries, while Google Ads capture users actively searching for solutions.
2. Consider Budget and Goals: Assess your budget constraints and advertising goals. If brand visibility and reaching decision-makers are paramount, LinkedIn might be more suitable. If capturing users at the point of intent is crucial, Google Ads may be preferred.
How to get started with advertising on linkedIn?
Getting started with advertising on LinkedIn involves several key steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you launch your first LinkedIn ad campaign:
1. Set Clear Objectives:
Define your advertising goals. Whether it’s increasing brand awareness, driving website traffic, generating leads, or boosting engagement, having clear objectives will guide your campaign strategy.
2. Create a LinkedIn Ad Account:
If you don’t already have a LinkedIn Ad account, go to the LinkedIn Campaign Manager and create one. You’ll need to link it to your LinkedIn Company Page.
3. Define Your Target Audience:
Use LinkedIn’s targeting options to define your audience. You can target based on job title, industry, company size, location, and more. The more specific you can be, the better you can reach your desired audience.
4. Choose Ad Format and Placement:
LinkedIn offers various ad formats, including sponsored content, sponsored InMail, display ads, and more. Select the format that aligns with your campaign goals. Consider where you want your ads to appear, such as in users’ feeds, on the right rail, or in InMail.
5. Set Your Budget and Bidding Strategy:
Determine your daily or total budget for the campaign. LinkedIn allows you to bid using either cost per click (CPC) or cost per thousand impressions (CPM). Choose the bidding strategy that aligns with your goals and budget.
6. Create Compelling Ad Content:
Develop engaging visuals and compelling ad copy. Your ad should be attention-grabbing and relevant to your target audience. Test different variations to see what resonates best.
7. Add a Call-to-Action (CTA):
Clearly state what action you want users to take after seeing your ad. Whether it’s visiting your website, downloading a resource, or contacting your company, a strong CTA is crucial for campaign success.
8. Set Up Conversion Tracking:
Implement LinkedIn Insight Tag on your website to track conversions. This allows you to measure the effectiveness of your campaigns and understand the actions users take after clicking on your ads.
9. Review and Launch:
Double-check all your settings, targeting options, and ad content. Once you’re satisfied, launch your campaign. Keep in mind that LinkedIn may take some time to review and approve your ads.
10. Monitor and Optimize:
Regularly monitor the performance of your ads using the Campaign Manager dashboard. Pay attention to key metrics like click-through rate (CTR), engagement, and conversion rates. Use this data to optimize your campaign by adjusting targeting, budget, and creative elements as needed.
11. A/B Testing:
Test different variations of your ads to identify what works best. Experiment with different headlines, visuals, ad copy, and CTAs to refine your strategy and improve performance.
Conclusion
Advertising on LinkedIn can be a valuable strategy for businesses aiming to connect with a professional audience, particularly in B2B contexts. To get started, it’s crucial to define clear objectives, create a LinkedIn Ad account, and carefully target your audience using LinkedIn’s robust targeting options.
Choose the appropriate ad format, set a budget and bidding strategy, and craft compelling ad content with a strong call-to-action. Implement conversion tracking to measure campaign effectiveness and regularly monitor performance metrics. A/B testing can help refine your approach over time. While LinkedIn advertising may be relatively more expensive, the platform’s unique audience and precise targeting capabilities can deliver meaningful results when executed strategically.
Continuous optimization and adaptation based on performance data are key to achieving a successful LinkedIn ad campaign.



